1. 기존 파드의 yaml 디스크립터 살펴보기
1) 2장에서 실행중인 배포의 전체 yaml 가져오기
[쿠버네티스 인 액션] 2장. 도커와 쿠버네티스 첫걸음 - 쿠버네티스에 첫 애플리케이션 실행 (tistory.com)
[쿠버네티스 인 액션] 2장. 도커와 쿠버네티스 첫걸음 - 쿠버네티스에 첫 애플리케이션 실행
1. node.js 애플리케이션 구동 : 래플리케이션 컨트롤러 생성 1) 레플리케이션 컨트롤러 생성 책에서는 이렇게 나오지만 deprecated 된 거라고 한다. kubectl run kubia --image=sootoance/kubia --port=8080 --generat
ddoance.tistory.com
kubectl delete deployments kubia
kubectl create deployment kubia --image=sootoance/kubia
kubectl get pods # name 확보
kubectl get pods kubia-985c88848-7bllg -o yaml
[ 전체 yaml ]
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2024-08-28T15:36:45Z"
generateName: kubia-985c88848-
labels:
app: kubia
pod-template-hash: 985c88848
name: kubia-985c88848-7bllg
namespace: default
ownerReferences:
- apiVersion: apps/v1
blockOwnerDeletion: true
controller: true
kind: ReplicaSet
name: kubia-985c88848
uid: 18961fb6-74e8-4692-bf63-a8ed61e2417d
resourceVersion: "254486"
uid: 450c1e01-9f78-40ca-96fe-848dc048a47f
spec:
containers:
- image: sootoance/kubia
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: kubia
resources: {}
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
terminationMessagePolicy: File
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount
name: kube-api-access-66lzj
readOnly: true
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst
enableServiceLinks: true
nodeName: minikube
preemptionPolicy: PreemptLowerPriority
priority: 0
restartPolicy: Always
schedulerName: default-scheduler
securityContext: {}
serviceAccount: default
serviceAccountName: default
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
tolerations:
- effect: NoExecute
key: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready
operator: Exists
tolerationSeconds: 300
- effect: NoExecute
key: node.kubernetes.io/unreachable
operator: Exists
tolerationSeconds: 300
volumes:
- name: kube-api-access-66lzj
projected:
defaultMode: 420
sources:
- serviceAccountToken:
expirationSeconds: 3607
path: token
- configMap:
items:
- key: ca.crt
path: ca.crt
name: kube-root-ca.crt
- downwardAPI:
items:
- fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
path: namespace
status:
conditions:
- lastProbeTime: null
lastTransitionTime: "2024-08-28T15:36:49Z"
status: "True"
type: PodReadyToStartContainers
- lastProbeTime: null
lastTransitionTime: "2024-08-28T15:36:45Z"
status: "True"
type: Initialized
- lastProbeTime: null
lastTransitionTime: "2024-08-28T15:36:49Z"
status: "True"
type: Ready
- lastProbeTime: null
lastTransitionTime: "2024-08-28T15:36:49Z"
status: "True"
type: ContainersReady
- lastProbeTime: null
lastTransitionTime: "2024-08-28T15:36:45Z"
status: "True"
type: PodScheduled
containerStatuses:
- containerID: docker://b485d4243b462eb97225a29939bc0437bc83939e44418a8f6616626f89d4f72a
image: sootoance/kubia:latest
imageID: docker-pullable://sootoance/kubia@sha256:e5333a523d345b0f276a148328abf0af8d1211f32a6c19f3336167d30dece69b
lastState: {}
name: kubia
ready: true
restartCount: 0
started: true
state:
running:
startedAt: "2024-08-28T15:36:49Z"
hostIP: 192.168.49.2
hostIPs:
- ip: 192.168.49.2
phase: Running
podIP: 10.244.0.11
podIPs:
- ip: 10.244.0.11
qosClass: BestEffort
startTime: "2024-08-28T15:36:45Z"
2) 파드를 정의하는 주요 부분
- metadata : 이름, 네임스페이스, 레이블 및 파드에 관한 기타 정보 포함
- spec : 파드 컨테이너, 볼륨, 기타 데이터 등 파드 자체에 관한 실제 명세
- status 파드 상태, 각 컨테이너 설명과 상태, 파드 내부 IP, 기타 정보 등 현재 실행 중인 파드에 관한 현재 정보 포팜
ㄴ 새 파드를 만들 때는 status 를 작성할 필요 없다. 읽기 전용의 런타임정보가 포함돼 있음
Reference
This section of the Kubernetes documentation contains references. API Reference Glossary - a comprehensive, standardized list of Kubernetes terminology Kubernetes API Reference One-page API Reference for Kubernetes v1.31 Using The Kubernetes API - overview
kubernetes.io
2. 파드 정의하는 yaml 만들기
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: kubia-manual
spec:
containers:
- name: kubia
image: sootoance/kubia
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
protocol: TCP
- 쿠버네티스 API v1 버전을 준수한다.
- 정의하는 리소스 유형은 파드이며 이름은 kubia-manual.
- 파드는 sootoance/kubia 이미지 기반 단일 컨테이너로 구성된다.
- 컨테이너 이름을 지정하고 8080포트에서 연결을 기다리는 것을 표시한다.
3. 도움이 되는 명령어
kubectl explain pods
kubectl explain pod.spec
4. kubectl create 명령어로 파드 만들기
kubectl create -f kubia-manual.yaml
kubectl get po kubia-manual -o yaml
kubectl get po kubia-manual -o json
kubectl get pods
5. 애플리케이션 로그 보기
docker logs <container ids>
kubectl logs kubia-manual
kubectl logs kubia-manual -c kubia # c : 컨테이너 이름 지정해서 가져오기
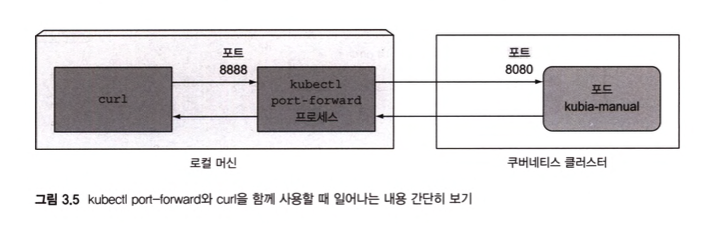
6. 파드 요청 보내기
- 서비스를 거치지 않고 (디버깅이나 다른 이유로) 특정 파드와 대화하고 싶을때 쿠버네티스는 해당 파드로 향하는 포워딩 구성
kubectl port-forward kubia-manual 8888:8080
- 포트 포워딩된 것을 확인할 수 있다.